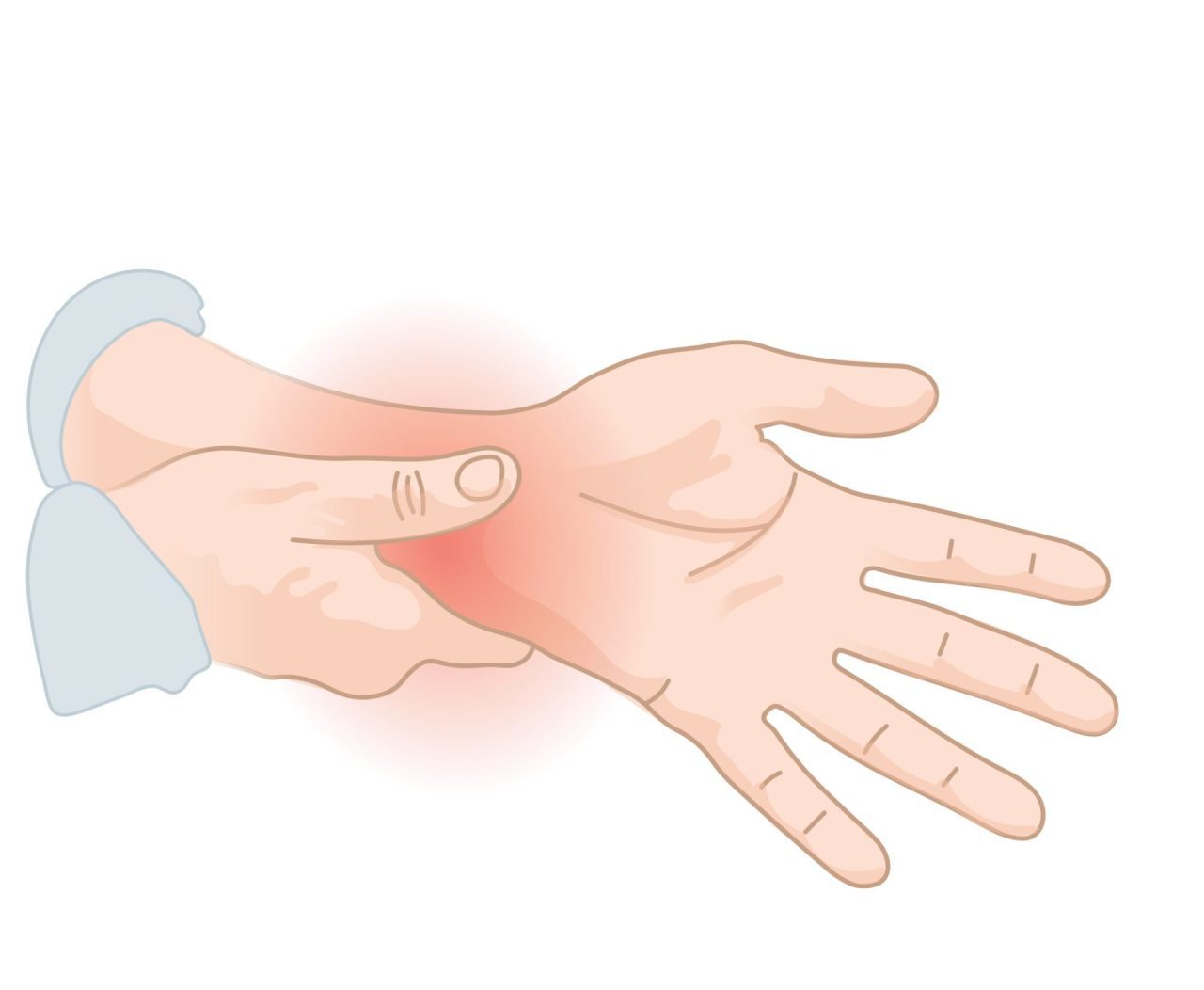
A TFCC (Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex) injury is a condition that affects the wrist and involves damage to the cartilage and ligaments on the ulnar side of the wrist joint. The TFCC provides stability and cushioning between the ulna bone, wrist bones, and the hand. TFCC injuries can occur due to trauma, repetitive use, or degenerative changes.
Managing a TFCC injury requires a comprehensive approach to reduce pain, promote healing, and restore function. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment process, helping individuals alleviate symptoms, improve wrist stability and strength, and prevent reoccurrence.
The treatment of TFCC injuries typically involves the following 5 stages of rehab:
- Pain management: The initial focus is on reducing pain and inflammation in the affected area. Physiotherapists may employ techniques such as manual therapy, including soft tissue massage and joint mobilization, to alleviate pain. They may also recommend the use of ice therapy and the use of a splint or brace to provide support and reduce stress on the injured TFCC.
- Range of motion: Once pain and inflammation are under control, the emphasis shifts to restoring normal range of motion in the wrist joint. Physiotherapists prescribe gentle stretching and range of motion exercises to improve flexibility and alleviate stiffness. These exercises aim to gradually increase the wrist’s mobility without exacerbating the symptoms.
- Motor control: This stage focuses on improving neuromuscular control and stability in the wrist joint. Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises to enhance muscle activation and coordination in the forearm and hand. Proprioceptive training and exercises that challenge balance and coordination are often incorporated to improve motor control and joint stability.
- Strengthening: Strengthening the muscles around the wrist and forearm is crucial for promoting healing and preventing future episodes of TFCC injury. Range physiotherapists will design a personalized exercise program that targets the muscles involved in wrist extension, flexion, and rotation. This may include resistance exercises using bands, weights, or specialized equipment to gradually build strength and endurance of the wrist.
- Maintenance: The final stage focuses on maintaining the gains achieved through rehabilitation and preventing recurrence. Range physiotherapists will provide guidance on protecting the wrist joint, modifying activities to reduce stress on the TFCC, and incorporating regular strengthening and flexibility exercises into daily routines. They may also provide advice on proper ergonomics and techniques for specific activities to prevent reinjury.
In addition to physiotherapy, other treatment options for TFCC injuries may include the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections or even surgery may be necessary, especially for severe TFCC injuries.
It is important to work closely with a qualified physiotherapist who specializes in treating TFCC injuries. Range physiotherapists will assess your condition, develop a tailored treatment plan based on the stages of rehab, and monitor progress throughout the rehabilitation process. With proper treatment, exercises, and modifications to activities, individuals with TFCC injuries can experience significant pain reduction, improved wrist function, and a return to their desired level of activity.
For more information regarding TFCC please see: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537055/ https://www.healthline.com/health/tfcc-tear