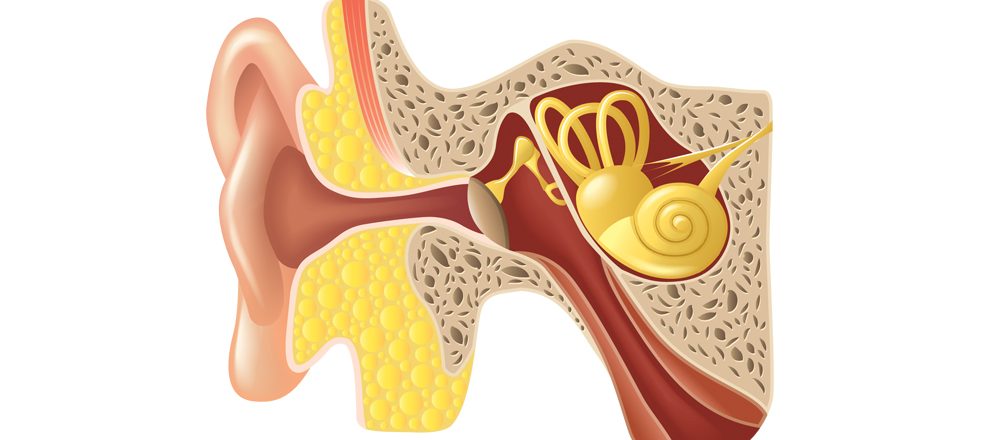
Positional vertigo, also known as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), is a common condition that causes brief episodes of dizziness or spinning sensations triggered by changes in head position. It occurs when small calcium crystals in the inner ear become dislodged and stimulate the balance organs in an abnormal way. Positional vertigo can be quite bothersome and affect an individual’s balance and quality of life.
Managing positional vertigo involves a specific approach to repositioning the displaced calcium crystals and restoring normal balance function. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment process, helping individuals recover from positional vertigo and regain their sense of balance.
The treatment of positional vertigo typically involves the following five stages of rehab:
- Assessment and diagnosis: The initial step is a thorough assessment and diagnosis by a physiotherapist specializing in vestibular rehabilitation. They will evaluate the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and perform specific tests, such as the Dix-Hallpike manoeuver, to determine the affected ear and the specific type of positional vertigo.
- Canalith repositioning maneuvers: Once diagnosed, the physiotherapist will perform canalith repositioning manoeuvers, such as the Epley manoeuver or Semont manoeuver. These manoeuvers involve specific head and body movements to guide the dislodged calcium crystals back to their proper position in the inner ear. The goal is to alleviate vertigo symptoms and restore normal balance function.
- Balance and coordination exercises: After the canalith repositioning manoeuvers, the focus shifts to balance and coordination exercises. Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises that aim to improve balance control, coordination, and reduce dizziness symptoms. These exercises may include gaze stabilization exercises, standing balance exercises, and walking exercises, among others. The goal is to train the brain to adapt to positional changes and promote long-term balance improvement.
- Vestibular rehabilitation exercises: In this stage, the emphasis is on targeted exercises that stimulate the vestibular system, which plays a crucial role in balance and spatial orientation. Range Physiotherapists will prescribe exercises such as vestibular ocular reflex (VOR) exercises, habituation exercises, and balance retraining exercises. These exercises aim to enhance the brain’s ability to process and integrate sensory information, improving overall balance and reducing the frequency and intensity of vertigo episodes.
- Maintenance and prevention: The final stage focuses on maintaining the gains achieved through rehabilitation and implementing strategies to prevent future episodes of positional vertigo. Range Physiotherapists can provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, such as sleeping with an elevated head position and avoiding certain head positions or movements that can trigger vertigo. They may also recommend ongoing home exercise programs to maintain vestibular function and promote long-term stability.
It is important to work closely with a qualified physiotherapist who specializes in vestibular rehabilitation. A Range Physiotherapist will assess the individual’s condition, develop a personalized treatment plan based on the stages of rehab, and provide ongoing support throughout the rehabilitation process. With proper treatment, exercises, and adherence to preventive strategies, individuals with positional vertigo can experience a significant reduction in symptoms, improved balance, and a better quality of life.