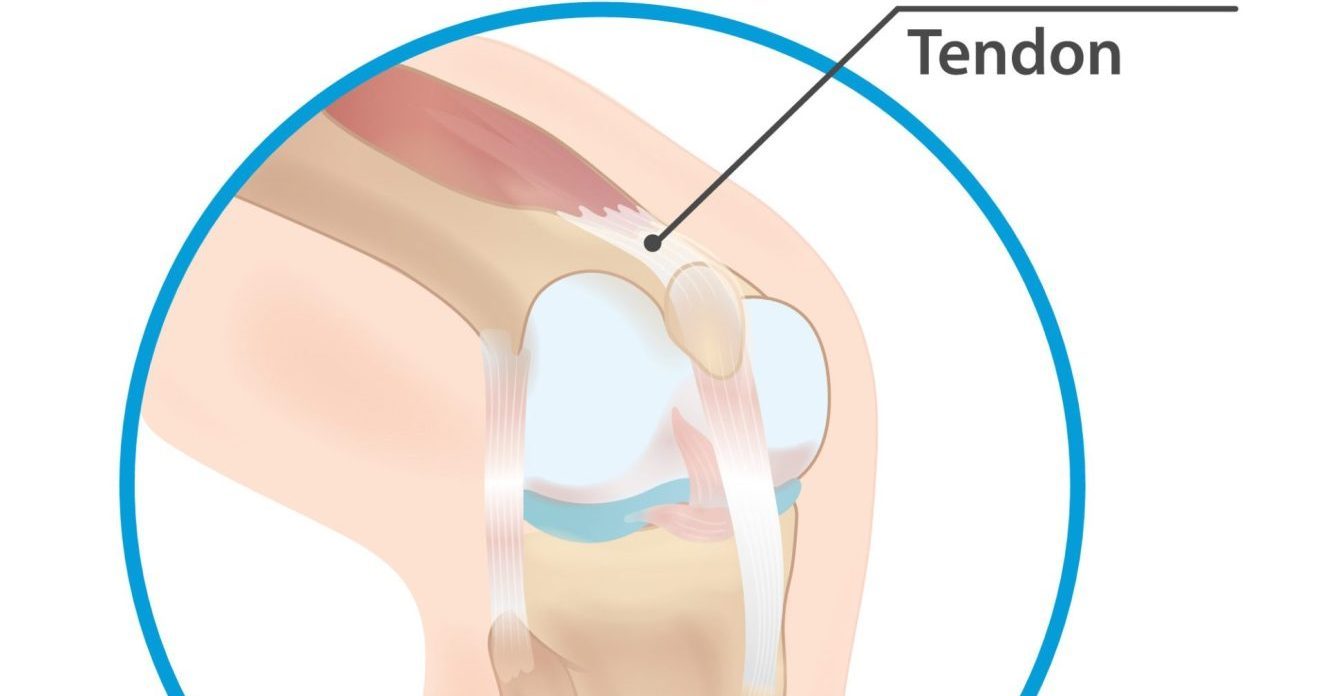
Quadriceps tendinopathy is a condition that affects the quadriceps tendon, which connects the quadriceps muscle to the kneecap (patella). It is a common overuse injury that can occur in athletes who participate in sports that involve jumping and running, such as basketball and volleyball. Quadriceps tendinopathy can cause pain, weakness, and limited function in the knee joint.
The management of quadriceps tendinopathy involves a combination of physiotherapy, medications, and rest. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and restore function and mobility in the knee joint.
Applying the 5 stages of rehab to quadriceps tendinopathy can help to achieve the best possible outcome as follows:.
Pain and symptom management: The primary goal is to reduce pain and inflammation. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are often recommended in the initial stages of treatment. Pain-relieving medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation. Physiotherapy treatments such as soft tissue massage, and taping can also help to reduce pain and swelling.
Range of motion: Once pain and inflammation are under control, the focus shifts to restoring normal range of motion in the knee joint. Physiotherapy treatments such as gentle mobilization, stretching exercises, and joint mobilization techniques can help to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in the knee joint.
Motor control: In stage 3, the focus is on improving neuromuscular control around the knee joint. Exercises that target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, can help to improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination. Hip exercises can also be beneficial in improving motor control, as the muscles around the hip joint play an important role in force distribution through the knee joint and tendons, and can assist in reducing the load on the quadriceps tendon when returning to full function.
Strengthening: In stage 4, the goal is to build strength in the muscles around the knee joint to improve stability and reduce the risk of reinjury. Resistance training, including exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg presses, can help to build muscle strength and endurance. Eccentric training, which involves lengthening the muscle under load, has been shown to be particularly effective in treating quadriceps tendinopathy.
Maintenance: In the final stage of rehab, the focus is on maintaining the gains achieved in the previous stages and preventing reinjury. This may involve continuing with regular exercise, including strengthening and proprioceptive training, as well as making any necessary modifications to daily activities or sports participation to reduce the risk of further injury.
It is important to note that the management of quadriceps tendinopathy may take several weeks to months to resolve and requires patience and commitment to the rehabilitation program. With proper treatment and rehabilitation, most people with quadriceps tendinopathy can return to their normal activities and sports with minimal to no pain or functional limitations.