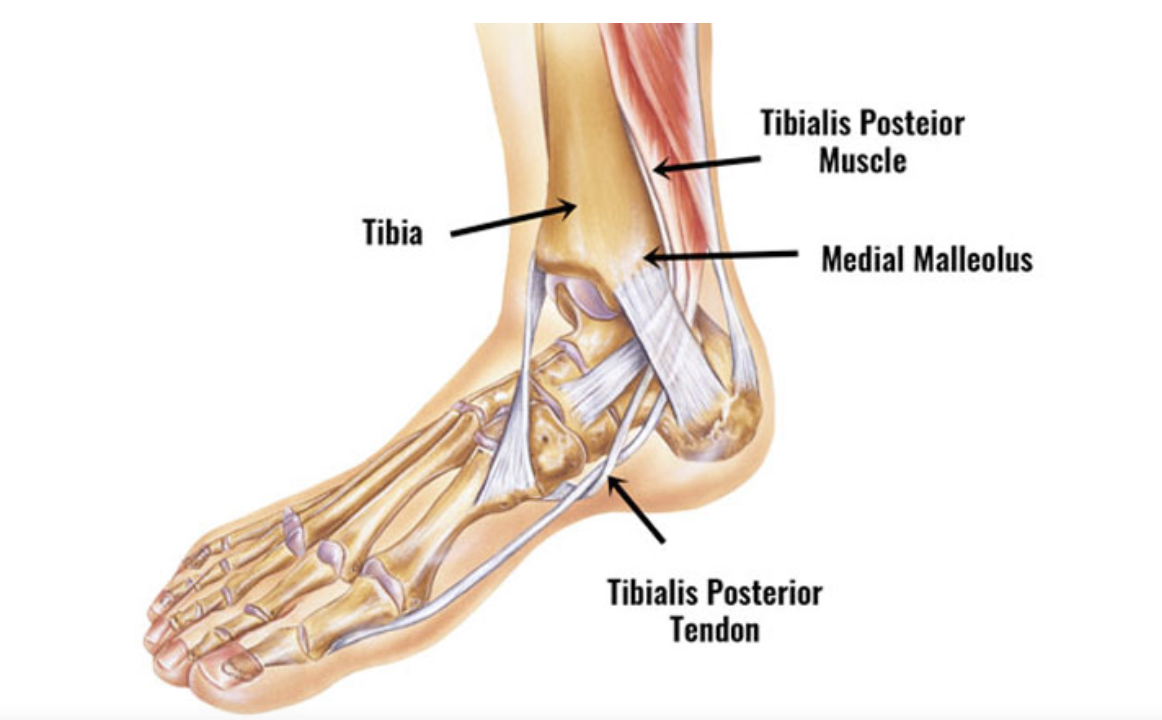
Tibialis posterior tendinopathy is a condition characterized by pain, inflammation, and dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle and foot. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of the foot and controlling foot and ankle movements. Tibialis posterior tendinopathy can occur due to overuse, repetitive activities, foot imbalances, or previous ankle injuries.
Managing tibialis posterior tendinopathy involves a comprehensive approach to reduce pain, promote healing, restore function, and prevent further injury. By applying the 5 stages of rehabilitation, individuals with tibialis posterior tendinopathy can effectively recover and regain optimal foot and ankle function.
- Pain management: The first stage focuses on managing pain and reducing inflammation in the affected tendon. Physiotherapists may employ modalities such as supportive taping, orthotics, manual therapy techniques, ice, or heat therapy to alleviate pain and promote healing. They may also recommend over-the-counter pain medications or prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Range of motion: Once pain is under control, the emphasis shifts to restoring normal range of motion in the ankle and foot. Physiotherapists prescribe gentle stretching and range of motion exercises to improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and prevent further tendon irritation. These exercises aim to gradually increase the mobility of the ankle joint and the flexibility of the tibialis posterior tendon.
- Motor control and balance: This stage focuses on improving motor control, proprioception, and balance to enhance foot and ankle stability. Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises that target the muscles around the ankle and foot, including the tibialis posterior muscle and other foot and ankle stabilizers. These exercises may include balance training, proprioceptive exercises, and coordination drills to improve joint control and prevent abnormal movement patterns.
- Strength training: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the ankle and foot is crucial for providing support and stability to the tibialis posterior tendon. Range Physiotherapists will design a personalized exercise program that targets the tibialis posterior muscle, calf muscles, and other foot and ankle muscles. These exercises may include resisted ankle inversion, calf raises, foot arch strengthening exercises, and other specific strengthening exercises to gradually build strength and improve tendon support.
- Maintenance and prevention: The final stage focuses on maintaining the gains achieved through rehabilitation and implementing strategies to prevent future tibialis posterior tendinopathy. Range Physiotherapists will provide guidance on proper footwear, orthotics, and modifications to prevent excessive stress on the tendon. They may also assess movement patterns and provide recommendations on activity modifications and gradual return to sports or activities to avoid re-injury.
Working closely with a qualified physiotherapist who specializes in foot and ankle rehabilitation is crucial. Range Physiotherapists will assess the severity of the tendinopathy, develop a personalized treatment plan based on the 5 stages of rehabilitation, and monitor progress throughout the process. With proper treatment, exercises, and adherence to preventive strategies, individuals with tibialis posterior tendinopathy can experience pain reduction, improved foot and ankle function, and a reduced risk of further tendon irritation.
For more information regarding tibialis posterior tendinopathy please see: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Tibialis_Posterior?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Posterior_Tibial_Tendon_Dysfunction